About hematopoietic- stem cells
Technology & InnovationWhat are hematopoietic stem cells
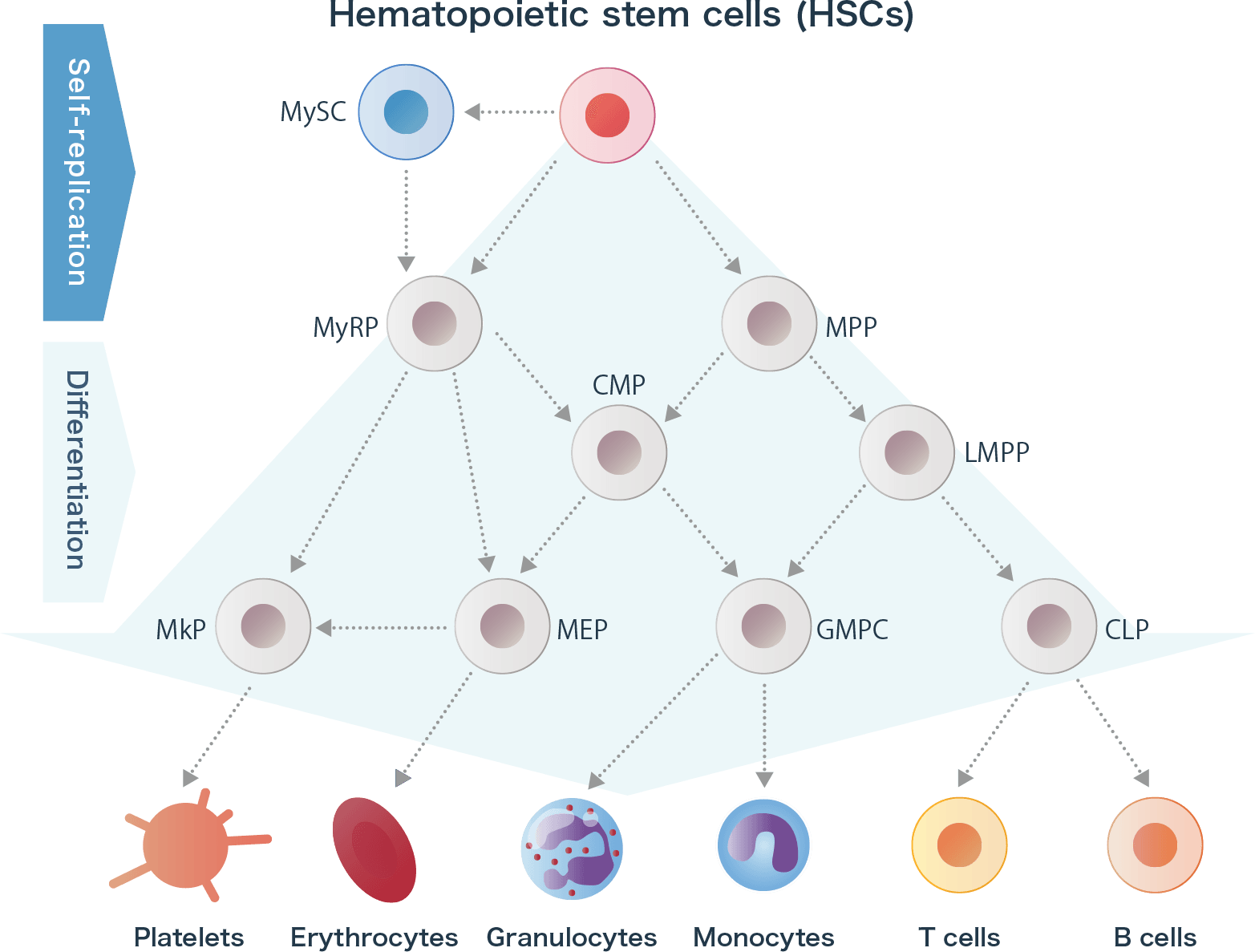
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are cells that are found mainly in bone marrow, and can grow into various different blood cells, such as red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes) and platelets, and are said to be the very source of blood. In addition, HSCs have the property of replicating themselves, and it is this that enables them to continuously produce blood.
The growing need for the application of
hematopoietic stem cells in cell therapy
Making use of the characteristics of HSCs, one type of cell therapy that has been carried out for many years is HSC transplantation.*
What is cell therapy
Cell therapy is a major medical therapy whose application has expanded rapidly in recent years in the field of regenerative medicine, known for iPS cells. It is a therapy that uses cells harvested either from the patient themselves or from others, and aims to treat the target disease by transplanting cells that have a range of different functions.
What is HSC transplantation
HSC transplantation is a therapy that involves the transplanting of healthy HSCs into patients suffering from blood cancers or disorders of the blood or immune system, in order to regrow healthy blood, and is a typical example of cell therapy.
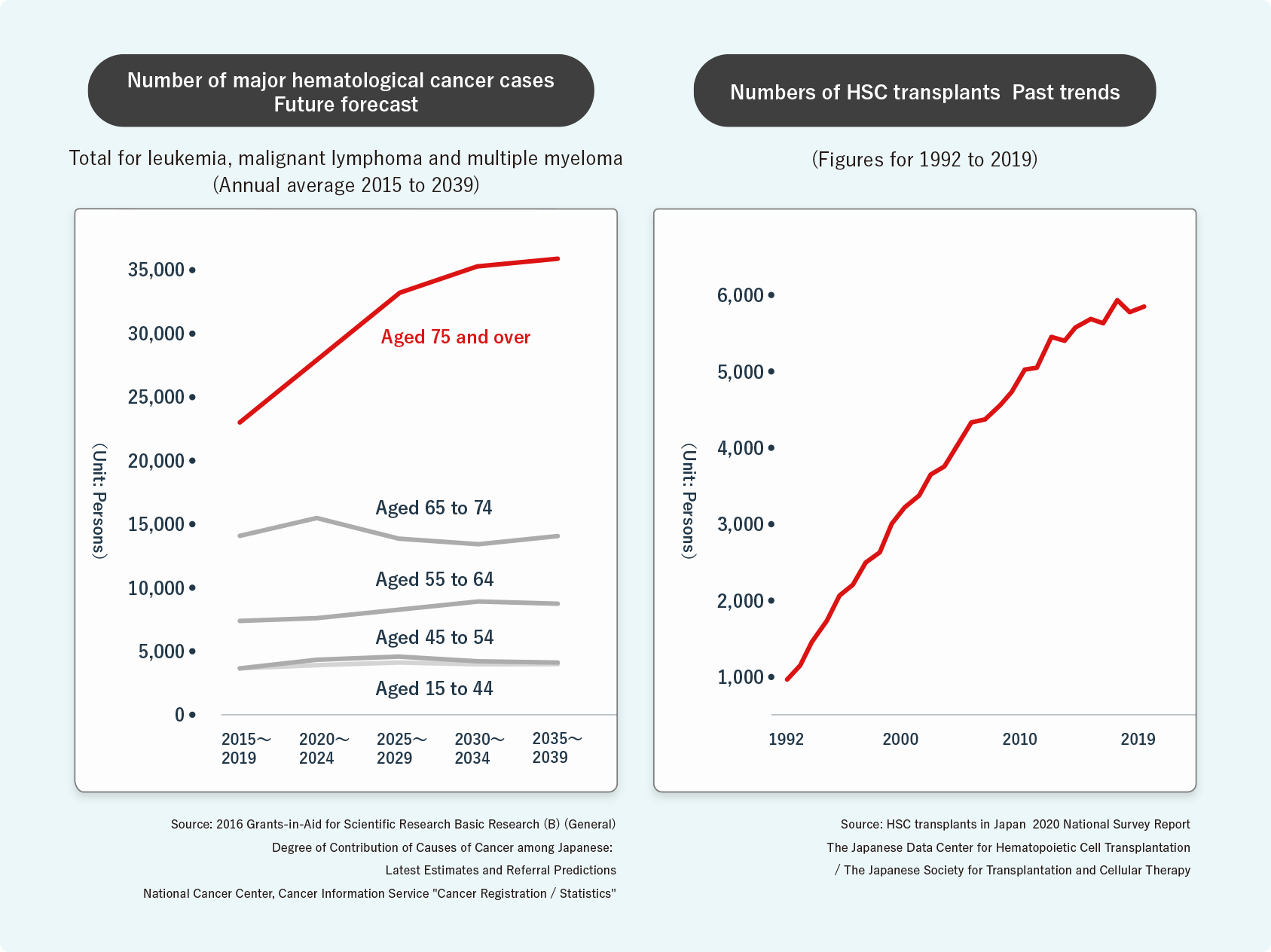
The number of hematological cancer patients requiring HSC transplantation is increasing, not only in Japan but also around the world. It is said that the main reason for this is that the prevalence of blood cancer increases with aging, but various other factors have also been pointed out.
Also, in addition to blood cancer, HSC transplantation is also used in the treatment of patients suffering from intractable diseases, such as aplastic anemia and severe combined immune deficiency. Furthermore, as a new method of treatment, it is expected to find application in gene therapy, in combination with gene editing technology. Several methods exist. For example, in gene therapy by the ex-vivo method (where gene transfer is performed in-vitro), abnormal HSCs are extracted from a patient suffering from blood system and immune system disorders, then corrected and normalized using gene editing, and then re-transplanted into the patient. In this way, it is expected that there will be continued further expansion of the application of cell therapy using HSCs.
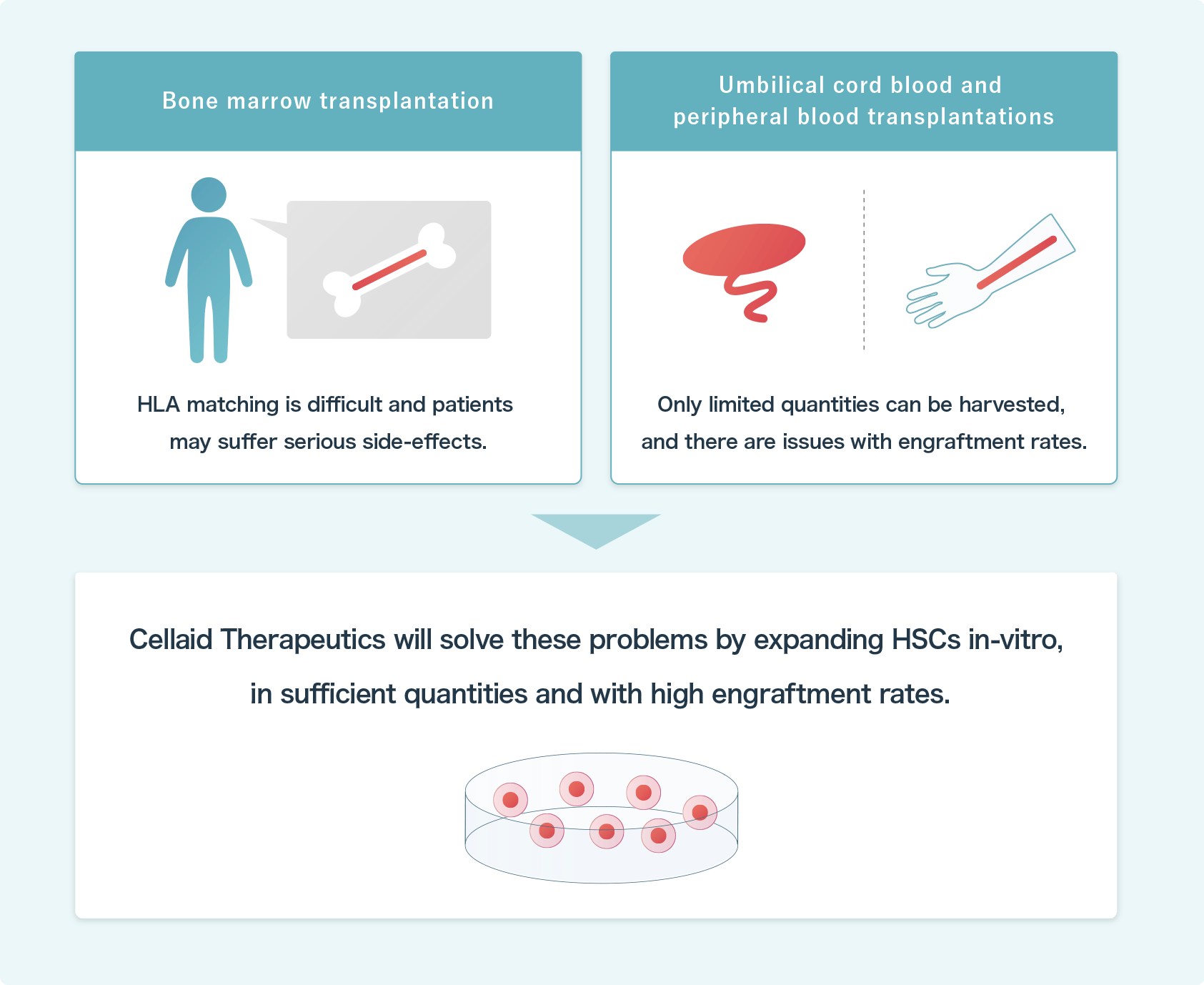
Challenges in hematopoietic stem cells transplants
There are two types of HSC transplantation, one that uses the patient's own HSCs and the other that uses the HSCs of others.
A typical treatment method involving the latter is "bone marrow transplantation", but the donor must be a person who matches the patient's "HLA (human leukocyte antigen)" type, which makes matching difficult, and the physical toll on the donor is significant. Also, there is a risk that the patient will suffer from serious side effects (GVHD: graft versus host disease), so there still remain serious challenges to be overcome.
Meanwhile, in peripheral blood and umbilical cord blood transplantations, of which much is expected as a treatment other than bone marrow transplantation, the number of original hematopoietic stem cells that can be harvested is limited, and there are still issues in terms of engraftment rate and quality.
In order to resolve the issues described above, an effective strategy will be to artificially increase HSCs in-vitro, and the technologies of Celaid Therapeutics will make it possible to produce the required volume of HSCs at the required time, with excellent engraftment rates (therapeutic effect) and quality.